Cov txheej txheem:
- Kauj Ruam 1: Txheeb Xyuas La IP Que Quiero Para El Dispositivo
- Kauj Ruam 2: Txiav Txim La Dirección De Salida Del Router (Rooj vag)
- Kauj Ruam 3: Averiguar La Dirección Del Servidor DNS
- Kauj Ruam 4: Anota Los Datos a Utilizar
- Kauj Ruam 5: Método Con Archivo /etc/dhcpcd.conf
- Kauj Ruam 6: Reinicia El Raspberry Pi
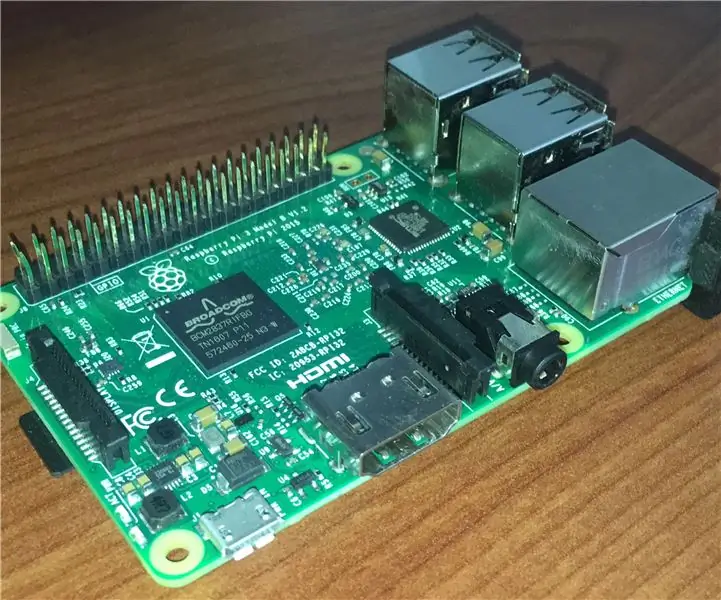

Video: Dirección IP Estática En Raspberry Pi (IP Static IP Address RaspberryPi): 6 Cov Kauj Ruam

2024 Tus sau: John Day | [email protected]. Kawg hloov kho: 2024-01-30 09:27

Teeb tsa tus IP chaw nyob zoo li qub
Este tutorial ha sido un resumen de la amplia explicación hecha por MadMike en inglés. Para más información él posee una amplia explicación de cómo realizar inclusive más variantes de las que acá se muestran.
Ntsib neeg Antes de comenzar
Es debido recordar que configurar una dirección IP estática no es siempre recomendable. Sobre todo porque son uno de los principales problemas para los administradores de liab. Ua txhaum txoj cai lij choj uas tsis muaj kev txwv tsis pub dhau IP tus neeg saib xyuas es necesaria.
Kauj Ruam 1: Txheeb Xyuas La IP Que Quiero Para El Dispositivo
El primer paso es averiguar cuál será la ip que queremos para colocarle al Raspberry Pi. Para esto abrimos el Terminal (en el Raspberry Pi) y escribimos lo siguiente:
ip -4 ntxiv qhia | grep ntiaj teb no
Si tienes el raspberry conectado solamente la la liab WiFi te deberá salir algo así:
inet 192.168.1.10/24 brd 192.168.1.0 tau thoob ntiaj teb wlan0
Entonces la primer seguida de números será tu dirección ip, hasta donde está el '/'.
Luego del '/' sawv cev rau el tamaño de la red, yog qhov muaj tseeb que la tuya también hiav txwv 24.
La segunda seguida de números (brd) sawv cev rau la dirección tshaj tawm de la liab.
Kauj Ruam 2: Txiav Txim La Dirección De Salida Del Router (Rooj vag)
Para determinar el gateway del router escribe la siguiente línea en el Terminal del Raspberry Pi:
ip txoj kev | grep default | awk '{print $ 3}'
Y eso devolverá una seguida de números que será la dirección de salida del router (Dirección Gateway)
Kauj Ruam 3: Averiguar La Dirección Del Servidor DNS
Normalmente la dirección DNS del servidor es zoo ib yam li igual a la dirección del Gateway. Para averiguarla sau ntawv siguiente línea en el Terminal del Raspberry Pi:
miv /etc/resolv.conf
Ah dev te devolverá dos datos el nombre de la red y la dirección DNS.
Kauj Ruam 4: Anota Los Datos a Utilizar
Anota los datos a utilizar que son:
- Cov lus qhia IP (puede ser la encontrada en el paso 1)
- El Gateway (suav nrog hauv pas pas 2)
- El Nameserver (suav nrog hauv pas pas 3)
Kauj Ruam 5: Método Con Archivo /etc/dhcpcd.conf
En el terminal del Raspberry Pi, sau ntawv rau siguiente línea para abrir el archivo correspondiente en el mismo Terminal:
nano /etc/dhcpcd.conf
Para configurar la ip que deseamos en la red WiFi a la que estamos logeados, buscamos un lugar donde escribir ahí en el archivo que se abrió y escribimos los datos del paso 4 (sustituyendo las XX que se ven a continuación):
wb wl0
zoo li qub ip_address = XX zoo li qub routers = XX zoo li qub domain_name_servers = XX
Kauj Ruam 6: Reinicia El Raspberry Pi
Ahora para reinicia el Raspberry Pi, debes escribir la siguiente línea en el terminal del Raspberry:
sudo kaw -r tam sim no
Y una vez que reinicie, cada vez que el Raspberry esté conectado a esa misma red, si la ip configurada está disponible, esta será asignada al Raspberry.
Pom zoo:
Hloov-Hloov Cov Khoom Ua Si: Cov Khoom Ua Si Cov Khoom Ua Si Ua Tau Zoo!: 7 Cov Kauj Ruam (nrog Duab)
Hloov-Hloov Cov Khoom Ua Si: Cov Khoom Siv Hluav Taws Xob Ua Tau Zoo!: Qho khoom ua si hloov pauv qhib txoj hauv kev tshiab thiab kev daws teeb meem kom tso cai rau menyuam yaus uas muaj lub cev muaj peev xwm txwv lossis kev xiam oos qhab kev loj hlob los cuam tshuam nrog cov khoom ua si ntawm nws tus kheej. Hauv ntau qhov xwm txheej, cov menyuam yaus uas xav tau cov khoom ua si hloov pauv tsis tuaj yeem nkag mus
RaspberryPi 3/4 Extension Board rau Ntxiv Cov Nta Ntxiv rau Raspberry Pi: 15 Cov Kauj Ruam (nrog Duab)

RaspberryPi 3/4 Extension Board rau Ntxiv Nta Ntxiv rau Raspberry Pi: peb paub tias raspberry pi 3/4 tsis tuaj nrog ua hauv ADC (analog to digital converter) thiab RTC (lub sijhawm tiag tiag) yog li kuv tsim PCB uas muaj 16 channel 12bit ADC, RTC, SIM7600 4G module, thawb cov nyees khawm, tso tawm, USB fais fab tawm, 5V fais fab tuag, 12V
ESP8266 Static IP (WIP): 3 Cov Kauj Ruam

ESP8266 Static IP (WIP): (Yog tias koj lub Wi-nkaus network twb tau teeb tsa hauv qee txoj hauv kev, koj yuav xav tham nrog koj Tus Thawj Saib Xyuas Haujlwm Network.) Ib feem ntawm lub hom phiaj ntawm peb tes num yog muab txhua ESP8266 nws tus kheej IP chaw nyob rau ua kom yooj yim dua kom taug qab cov cuab yeej thiab txuas
ESP32 Captive Portal los teeb tsa Static thiab DHCP IP Chaw: 8 Kauj Ruam
ESP32 Captive Portal los teeb tsa Static thiab DHCP IP Chaw: ESP 32 yog lub cuab yeej nrog WiFi ua ke thiab BLE. Nws yog qhov zoo rau IoT cov haujlwm. Tsuas yog muab koj tus lej SSID, tus lej zais thiab tus IP teeb tsa thiab muab cov khoom tso rau hauv huab. Tab sis, kev tswj hwm IP chaw thiab Tus neeg siv daim ntawv pov thawj tuaj yeem yog lub taub hau
Solidworks: Static Thermal Simulation: 4 Kauj Ruam
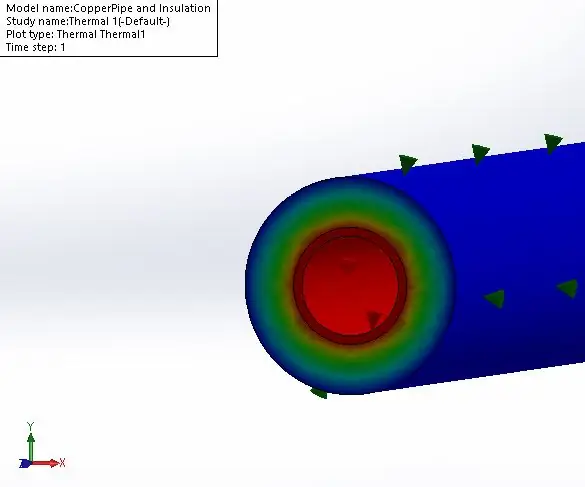
Solidworks: Static Thermal Simulation: Cov lus qhia no qhia txog yuav ua li cas thiaj ua tau yooj yim Static Thermal Analysis in Solidworks
